NASA’s Perseverance rover is busy just exploring Mars, looking for signs of ancient life.
Perseverance, nicknamed “Percy”, the centerpiece of NASA’s $2.7 billion Mars 2020 mission, touched down inside the Red Planet’s Jezero Crater on Feb. 18, 2021.
The car-sized robot is searching for evidence of past microbial life and has collected several dozen samples for future return to Earth, among other ambitious tasks.
“I don’t think we’ve had a mission that is going to contribute so much to both science and technology,” NASA Acting Administrator Steve Jurczyk told Space.com shortly before Perseverance touched down. “It’s going to be truly amazing.”
Related: How long does it take to get to Mars?
How big is the Mars rover?
Join our Mars talk!
Join our forums here to discuss the Perseverance rover on Mars. What do you hope finds?
If Perseverance looks familiar, that’s because the robotic explorer is largely based on its predecessor, the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Curiosity rover, which landed in August 2012 and is still going strong today.
Like Curiosity, the Perseverance rover was built by engineers and scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Roughly 85% of Perseverance’s mass is based on Curiosity’s “heritage hardware,” saving NASA time and money and reducing risk considerably, agency officials have said.
Perseverance is about 10 feet long (not including its robotic arm), 9 feet wide, and 7 feet tall (about 3 meters long, 2.7 meters wide and 2.2 meters tall). At 2,260 lbs. (1,025 kilograms), Perseverance weighs less than a compact car.
Like Curiosity, Perseverance has a rectangular body, six wheels, a robotic arm, a drill for sampling rocks, cameras and scientific instruments. But those instruments are quite different than the gear aboard Curiosity because the two rovers have divergent goals. Curiosity’s main task involves assessing the habitability of ancient Mars, whereas Perseverance will hunt for evidence of ancient Martians.
Perseverance’s seven instruments “build on the success of MSL, which was a proving ground for new technology,” said George Tahu, NASA’s Perseverance program executive. “These will gather science data in ways that weren’t possible before.”
Perseverance also used the same entry, descent and landing (EDL) strategy as Curiosity. Both rovers hit the Mars atmosphere at tremendous speeds, deployed a supersonic parachute after friction slowed them down enough, and were finally lowered gently to the red dirt on cables by a rocket-powered “sky crane.”
But Perseverance had some EDL upgrades that Curiosity did not enjoy. For example, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which manages the Mars 2020 mission, developed new landing technology called terrain-relative navigation. As the rover descended through the Martian skies, it used a computer to compare the landscape with pre-loaded terrain maps, guiding itself to a safe landing site and making corrections on the way down.
Another new feature, known as range trigger, used location and velocity information to determine when to open the supersonic parachute, narrowing the landing ellipse by more than half.
“Terrain-relative navigation enables us to go to sites that were ruled too risky for Curiosity to explore,” said JPL’s Al Chen, Perseverance’s EDL lead. “The ranger trigger lets us land closer to areas of scientific interest, shaving miles — potentially as much as a year — off a rover’s journey.”
Perseverance FAQs answered by an expert
We asked Ken Farley, Mars 2020 project scientist a few frequently asked question about the Perseverance rover.

Ken Farley is the W.M. Keck Foundation Professor of Geochemistry in the Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences at the California Institute of Technology. Farley is the project scientist for Mars 2020 where he leads the science team and worked with engineers to design and build the Perseverance rover.
What’s the difference between the Perseverance rover and other Mars rovers?
Perseverance is built from the same basic design as Curiosity, which landed on Mars about a decade before Perseverance. However, because Perseverance has a different objective, it is fitted out with different science instruments and capabilities.
For example, Perseverance is designed to seek possible evidence of ancient martian life, so includes instruments that can make microscopic-scale maps of elements and organic molecules in rocks which could provide such evidence. Perseverance is also the first step in a series of missions that could bring samples back to Earth for deeper study and specifically is tasked with collection of the samples. For that reason Perseverance carries a coring drill which acquires rock cores directly into individual sample tubes, and a sophisticated robotic system that then seals them tightly for their return journey.
How long will Perseverance last on Mars?
Although Perseverance was designed to last just a few years on Mars, it’s twin, Curiosity, is still going strong after almost 11 years of roving. Unlike the earlier rovers Spirit and Opportunity, Perseverance and Curiosity use a nuclear power source rather than solar panels that can fail when covered by dust or when the sun is dimmed by airborne dust during dust storm season.
Is the Perseverance rover coming back to Earth?
Nope. After its mission is completed, it will become a permanent marker of humankind’s journey beyond Earth. At present there is no known technology to launch the rover back to Earth, and in any case, doing so would surely cost more than just building a copy on Earth.
What discoveries has the Perseverance rover made?
The most exciting finding relates to the history of the body of water that once filled Jezero crater, perhaps 3.5 billion years ago, now long since dried up. Although the existence of such a lake was detected from orbital images acquired a few years ago, Perseverance can now add substantial detail to the crater’s history.
On the floor of the crater the rover discovered igneous rocks — produced by crystallizing magmas. These suggest the possibility that the crater was once filled with a lava lake, before the water lake. Sometime later, water flowed into the crater to produce a shallow lake on top of the igneous rocks, creating salty mudflats that were likely good habitats for any martian life that may have existed.
Later, the lake deepened, and we find evidence of a slowly flowing river winding back and forth in much the same way that rivers on Earth do. Finally, there was a period of river flooding that carried very large boulders into the crater.
All of this is important because it tells a story of a Mars very different from today. When the rocks Perseverance is exploring were created billions of years ago, Mars was active — it had volcanoes, lakes, rivers, and habitable environments. But today it is cold, dry, and quiet. Bringing samples back is the best way to understand how early Mars worked, and what happened to so vastly change it.
Perseverance rover science: Cameras, instruments and more
Perseverance boasts nearly five times more cameras than the first Mars rover. Sojourner, which landed in 1997, carried only five cameras, and the twin rovers Spirit and Opportunity, which hit the red dirt in 2004, had 10 cameras apiece. Curiosity has 17.
Perseverance has 23 cameras. Several of them filmed the rover’s Mars arrival, capturing its landing in historic and unprecedented detail. The epic EDL video shows Perseverance’s parachute snap open in the Martian sky, for example, and documents the moment the robot’s six wheels hit the red dirt.
“For those who wonder how you land on Mars, or why it is so difficult, or how cool it would be to do so — you need look no further,” Jurczyk said in a statement a few days after touchdown.
“Perseverance is just getting started and already has provided some of the most iconic visuals in space exploration history,” he added. “It reinforces the remarkable level of engineering and precision that is required to build and fly a vehicle to the Red Planet.”
Some of Perseverance’s cameras provide more color and 3D imaging than Curiosity can collect, according to Jim Bell of Arizona State University, the principal investigator for Perseverance’s Mastcam-Z camera system. “Z” stands for “zoom,” one of the improvements on Curiosity’s high-definition Mastcam.
Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity have all captured 1-megapixel images in black and white with their engineering cameras, which assist in drive planning and hazard avoidance. But Perseverance’s engineering cameras acquire high-resolution, 20-megapixel color images. Their wider field of view means that, instead of spending time taking multiple images to be stitched together on the ground, the new cameras capture the same view in a single snapshot. The cameras also reduce motion blur, so they can take photos while the rover is traveling.
More detailed images mean more data to beam through space.
“The limiting factor in most imaging systems is the telecommunications link,” said Perseverance imaging scientist Justin Maki of JPL, the instrument operations team chief. “Cameras are capable of acquiring much more data than can be sent back to Earth.”
Related: Perseverance rover snaps gorgeous HD panorama of Mars

Smarter rover cameras are helping to reduce the load. On Spirit and Opportunity, photo compression was done using the onboard computer. On Perseverance, as on Curiosity, compression is performed by electronics built into the camera.
Perseverance’s data is beamed back to Earth via several spacecraft orbiting Mars: NASA’s Mars Odyssey, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution), and the European Space Agency’s Trace Gas Orbiter.
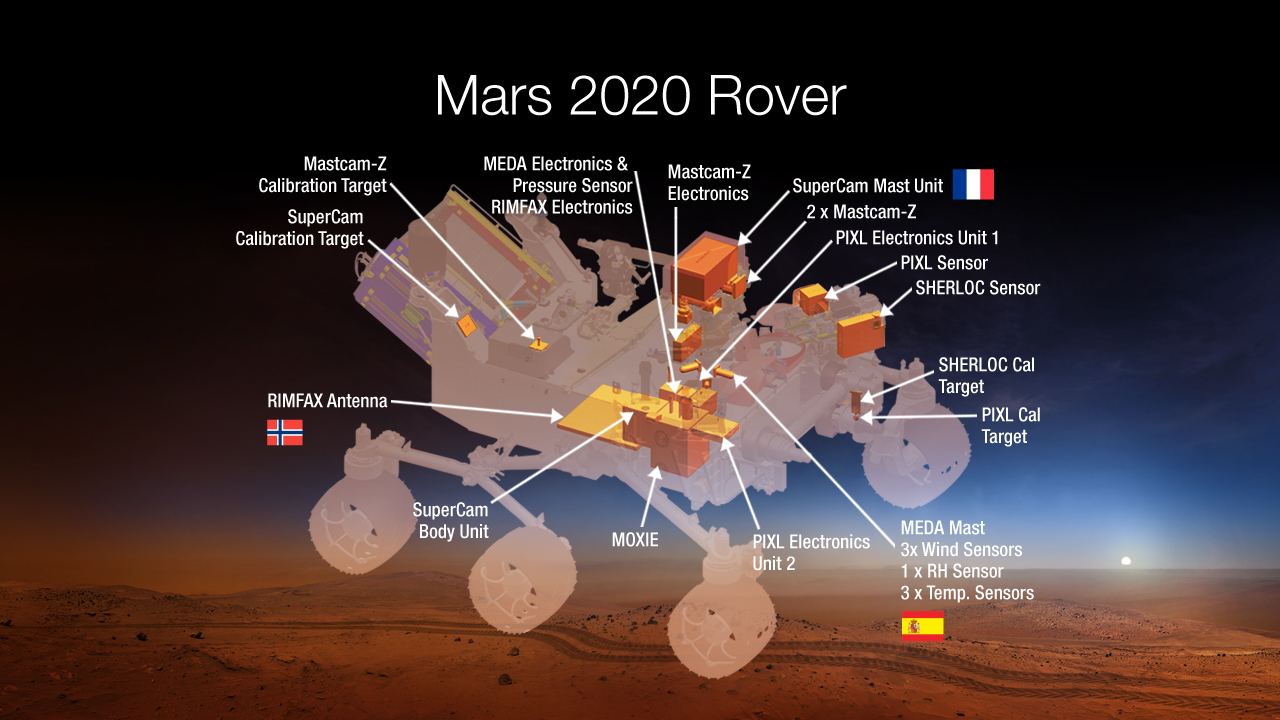
Mastcam-Z is one of Perseverance’s seven science instruments. Another, known as SHERLOC (“Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals”), is the first instrument on Mars to use Ramen and fluorescence spectroscopies, techniques familiar to forensics experts.
When ultraviolet light shines over certain carbon-based chemicals, they glow much like material beneath a black light. The glow can help scientists detect chemicals that form in the presence of life. SHERLOC is photographing the rocks it studies, then mapping the chemicals it detects across the images.
“This kind of science requires texture and organic chemicals — two things that our target meteorite will provide,” Rohit Bhartia of JPL, SHERLOC’s deputy principal investigator, said in a statement.
The space rock mentioned by Bhartia is the Martian meteorite Sayh al Uhaymir 008 (SaU008), which the team used to help calibrate SHERLOC. Previous rovers have included calibration targets, but none of them have ever relied on Martian meteorites. (A meteorite has, however, ridden to Mars aboard the Mars Global Surveyor, which ceased operations in January 2007.)
Related: 5 weird things NASA’s Perseverance rover took to Mars
Another Perseverance instrument, called PIXL (“Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry”), is determining the composition of Martian materials at a very fine scale using a high-resolution camera and X-ray fluorescence spectrometer.
The rover’s SuperCam instrument, an evolution of Curiosity’s ChemCam, zaps target rocks with lasers and determines the chemical composition of the resulting vapor.
Perseverance also carries a ground-penetrating radar instrument called RIMFAX (“Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment”). RIMFAX is the first rover instrument ever to look under the surface of Mars, mapping layers of rock, water and ice up to 33 feet (10 m) deep.
Also aboard the rover is a weather station known as MEDA (“Mars Environmental Data Analyzer”) and a technology demonstration called MOXIE (“Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment”).
MOXIE is designed to generate oxygen from the Red Planet’s atmosphere, which is 95% carbon dioxide by volume. Such gear, if scaled up, could help humanity get a foothold on the Red Planet in the future, NASA officials have said. (The agency aims to put boots on Mars in the 2030s.)
SHERLOC, PIXL and Perseverance’s rock drill sit at the end of the rover’s 7-foot-long (2.1 m) robotic arm, which can move with five degrees of freedom. MEDA, MOXIE and RIMFAX are on Perseverance’s body, and Mastcam-Z and SuperCam are on the rover’s headlike mast.
Perseverance rover’s Mars microphone
Perseverance also carries two microphones, to relay the sounds of the Red Planet back to Earth. One is part of the EDL camera system, and the other is built into SuperCam.
The mission team hoped the EDL mic would record sound during Perseverance’s touchdown. That didn’t happen, but the instrument did switch on shortly after landing, collecting the first-ever true audio on the surface of Mars. (Two other NASA Mars missions, the Mars Polar Lander and Phoenix lander, carried microphones, but neither of them returned any audio data. Mars Polar Lander crashed in December 1999, and Phoenix’s mic was never turned on, out of concern that it could interfere with the spacecraft’s May 2008 touchdown.)
Related: Listen to the Mars wind blow in these 1st sounds from the Perseverance
Hearing these otherworldly sounds helps bring Mars down to Earth for all of us, making the Red Planet a more accessible place, mission team members have said. And Mars audio has more than just gee-whiz appeal.
“There’s a lot of good science that can be done by having a microphone on Mars,” SuperCam team member Sylvestre Maurice, a planetary scientist at the Research Institute in Astrophysics and Planetology in France told Space.com.
For example, the SuperCam will help reveal how hard target rocks are and whether or not they have a coating. Martian audio is also helping improve our understanding of the Red Planet’s thin atmosphere, by providing data to plug into models.
It’s possible that Perseverance will even gather stereo sound on the Martian surface, by operating the EDL and SuperCam mics in concert.
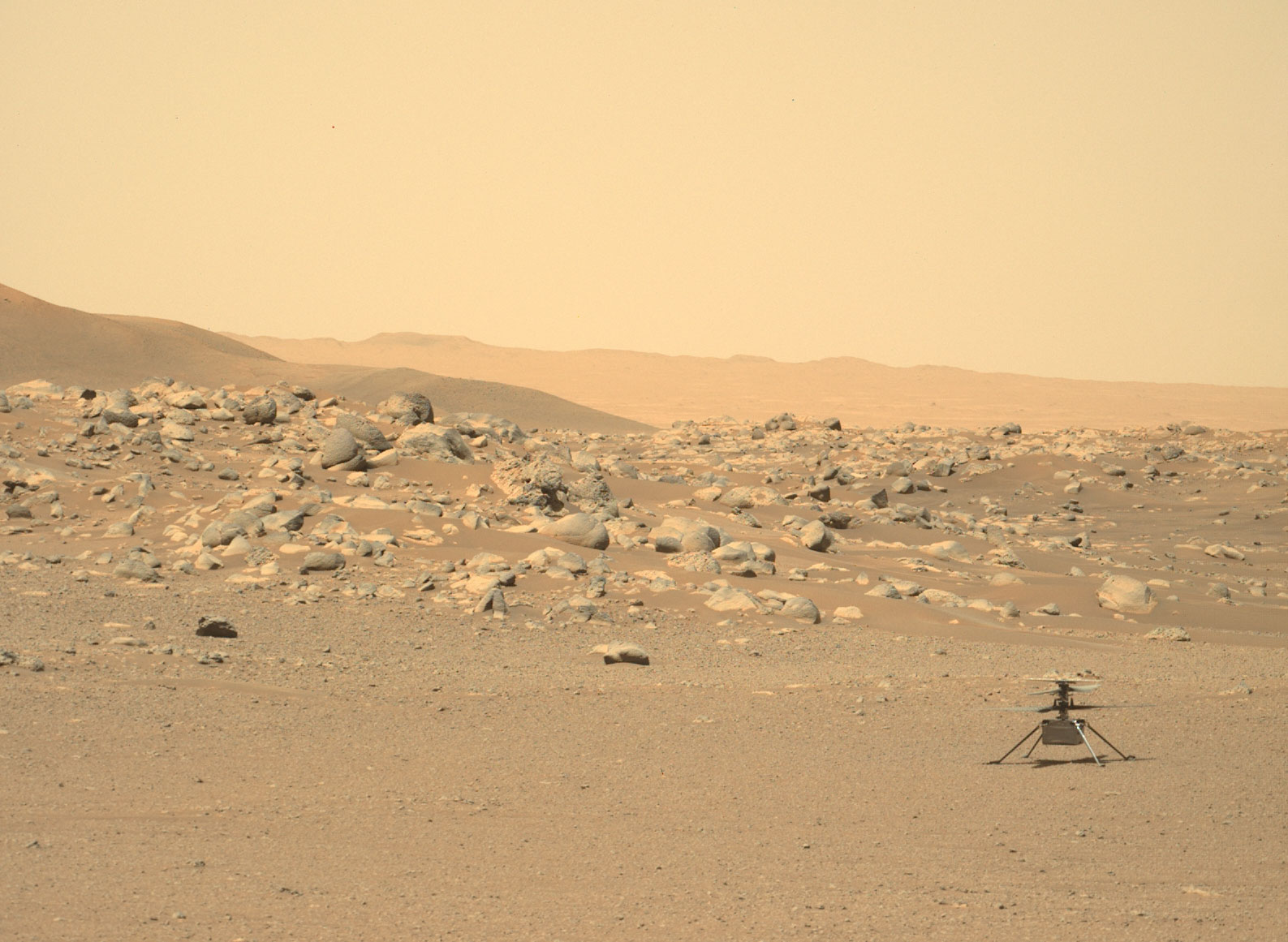
The first Mars helicopter: Ingenuity
Perseverance also carried a tiny hitchhiker to Mars — a 4-lb. (1.8 kg) helicopter named Ingenuity, which will attempt to make the first-ever rotorcraft flights on a world beyond Earth.
Like MOXIE, Ingenuity is a technology demonstration; it carries a high-resolution camera but no science instruments.
Related: NASA’s Mars helicopter Ingenuity takes off on historic 1st powered flight on another world
The chopper quickly aced its primary mission, a five-flight campaign designed to show that aerial exploration is feasible on Mars. Ingenuity then embarked on an extended mission, during which it’s serving as a scout for Perseverance.
Ingenuity has been conducting short flights on the Red Planet for over two years, and it’s still breaking records. On its 49th flight, the 4-pound (1.8 kilograms) chopper reached a top speed of 14.5 mph (23.3 kph) and a maximum altitude of 52.5 feet (16 meters), according to the mission’s flight log. The previous records were 13.4 mph (21.6 kph) and 46 feet (14 m), respectively.

Perseverance power: Its nuclear battery revealed
Spirit and Opportunity were solar-powered. Both rovers far outlived their three-month warranties, roaming the red desert for years. But they both ultimately succumbed to the elements, freezing to death after finding themselves in situations where their solar panels couldn’t soak up enough sun. (NASA declared Spirit and Opportunity dead in 2011 and 2019, respectively.)
Curiosity and Perseverance don’t have to worry about Martian sunlight levels. The big rovers are nuclear-powered, each sporting a roughly 100-lb. (45 kg) Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG).
These MMRTGs convert to electricity the heat naturally produced by the radioactive decay of plutonium-238. And they keep doing so for a long time; the MMRTG has an operational life of 14 years, according to NASA’s Mars 2020 information page.
Curiosity is still going strong inside Mars’ Gale Crater, more than eight years after touching down. So there’s every reason to believe that Perseverance’s power source, and its other vital components, will allow the robot to keep roaming beyond the rover’s prime mission duration of one Mars year, or about 687 Earth days.
Perseverance rover launch: Voyage to Mars in a pandemic
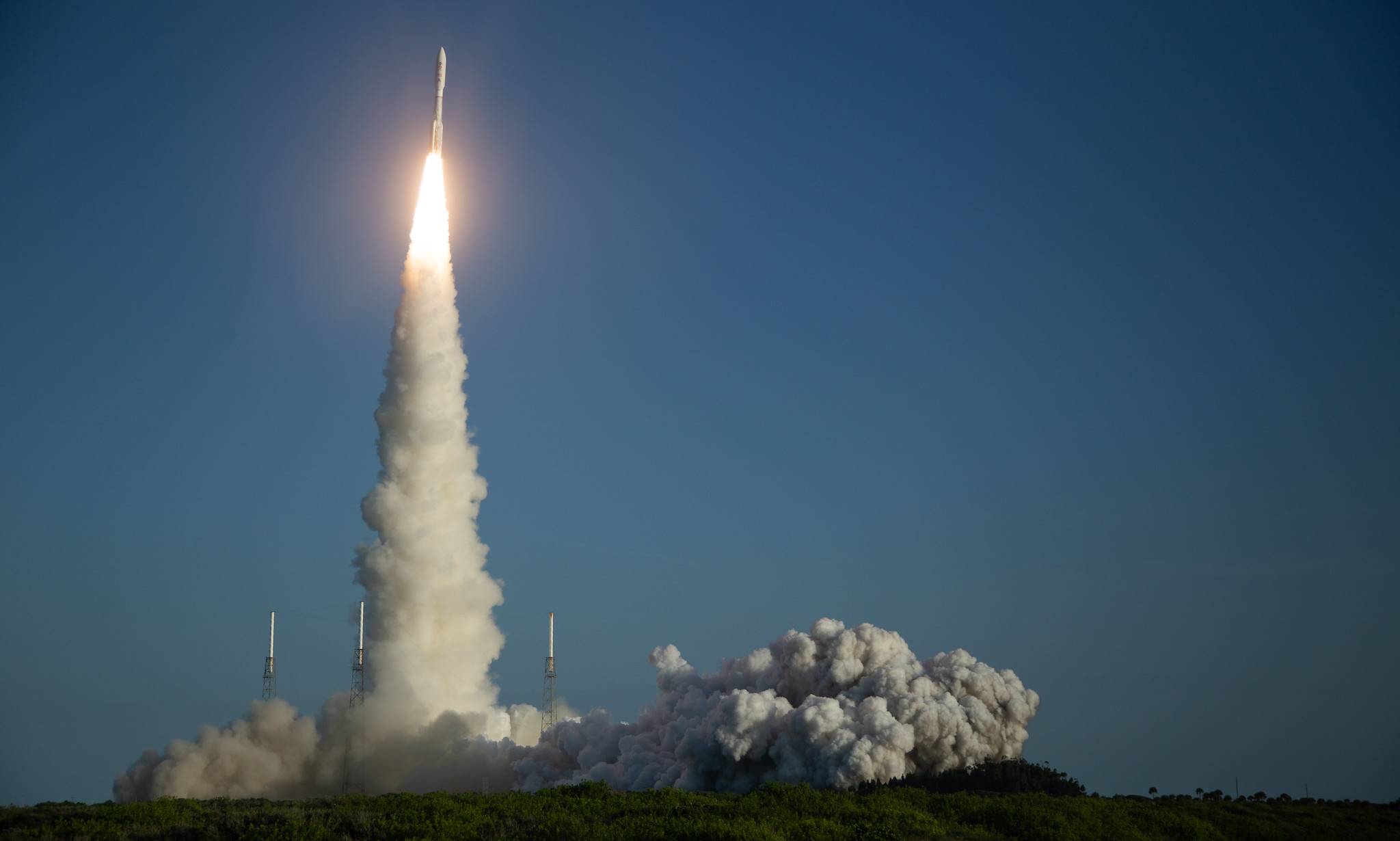

Perseverance launched from Florida’s Space Coast on July 30, 2020, hurtling into space atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
Getting off Earth is never easy, and Perseverance had a particularly challenging path. The mission team had to conduct the final assembly and testing procedures, and the launch itself, while the coronavirus pandemic raged around them.
Like the rest of us, many Perseverance team members had to adapt to working from home; key rover prep was done from living rooms, kitchens and backyard patios. And getting the robot to the launch pad on time — a high priority, since launch windows for Mars missions open for just a few weeks once every 26 months — was far from a foregone conclusion.
“In March and early April [2020], we weren’t sure we were going to be able to make it,” Jurczyk told Space.com. (Back then, the NASA administrator was Jim Bridenstine, and Jurczyk led the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate.) “But we were able to work through the planning and get there. It’s a real credit to the dedication and hard work of the team.”
Perseverance’s Mars landing at Jezero Crater
Perseverance’s deep-space journey went smoothly, and the rover arrived at Mars as planned, 6.5 months after liftoff. The pandemic was still an issue on landing day, however; rover team members assembled at mission control at JPL to oversee EDL on Feb. 18, but they wore masks and practiced social distancing to the extent possible.
In a harrowing “seven minutes of terror,” the rover plunged into the Martian atmosphere, jettisoned its heat shield and deployed the largest parachute ever built for Mars to slow its descent to the Martian surface. Cameras on the rover, its sky crane and backshell captured the descent down to the ground, including the moment the sky crane, hovering over the Martian surface, lowered Perseverance to the ground for a picture perfect landing.
The Perseverance rover landed safely on Mars and began surveying its Jezero Crater home.
In February 2017, a team of scientists narrowed the Mars 2020 landing-site candidates down to three finalists: Columbia Hills, Northeast Syrtis and Jezero Crater.
One site had been explored before. Starting in 2004, the Spirit rover roamed through Gusev Crater and Columbia Hills, where the robot discovered evidence of past water, the only place it found water in the enormous crater. Later data analysis suggested that the crater may have once hosted a shallow lake.
An ancient volcano in Northeast Syrtis could have generated hot springs and melting ice, creating the ideal conditions for past microbial life, researchers have said. The edge of the Syrtis Major volcano exposes 4-billion-year-old bedrock, as well as many minerals altered by volcanic activity during the Red Planet’s early history.
The 28-mile-wide (45 km) Jezero Crater, meanwhile, is an ancient lakebed where microbial life could have developed, NASA officials said in a statement. Jezero also harbors the remains of a long-gone river delta, whose structure suggests that water filled and drained from the site at least twice. MRO has also spotted minerals at the site that have been chemically altered by water.
In November 2018, NASA announced the final selection: Perseverance will explore Jezero Crater.
“The landing site in Jezero Crater offers geologically rich terrain, with landforms reaching as far back as 3.6 billion years old, that could potentially answer important questions in planetary evolution and astrobiology,” Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, said in a statement at the time.
“Getting samples from this unique area will revolutionize how we think about Mars and its ability to harbor life,” he added.
How the Perseverance rover will collect Mars samples
It’s possible that Perseverance will spot convincing signs of ancient life on the Martian surface — something akin to a fossilized stromatolite here on Earth, perhaps. That’s a tall order for a lonely robot on a faraway world, however, so it’s more likely that the rover’s life-hunting data will be suggestive at best, mission team members have said.
But Perseverance will allow scientists to get much better and more detailed looks at promising samples — by kicking off humanity’s first-ever Mars sample-return campaign.
Perseverance has been busy collecting various rock samples, filling sample tubes with rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). “The belly of the rover houses all the equipment and supplies needed to collect samples.
It contains a rotating drill carousel, which is a wheel that contains different kinds of drill bits,” NASA officials wrote in a description of Perseverance’s pioneering sample-collecting hardware.
“While the rover’s big arm reaches out and drills rock, the rover belly is home to a small robotic arm that works as a ‘lab assistant’ to the big arm,” they added. “The small arm picks up and moves new sample tubes to the drill, and transfers filled sample containers into a space where they are sealed and stored.”
The baseline sample-return architecture calls for Perseverance to deliver several dozen samples to a rocket-equipped NASA lander on the Red Planet. That rocket will then send the samples to Mars orbit, where they’ll be snagged and hauled to Earth by an ESA probe. Perseverance is the only one of these spacecraft that’s currently operational; the ESA orbiter and NASA lander are scheduled to launch in 2027 and 2028, respectively.
Although Perseverance is currently in good condition, the team also has a backup plan in case the rover is unable to deliver its onboard samples to a rocket-toting lander. The rover has deposited ten sample tubes on the surface, that could be recovered in the future by the Mars Sample Return campaign.
Related: The big reveal: What’s ahead in returning samples from Mars?
How Perseverance and Ingenuity got their names

NASA let school kids name the Sojourner, Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity rovers via a nationwide competition, and the agency continued this tradition with Mars 2020.
The winning name was nominated by Virginia seventh-grader Alex Mather and announced in March 2020. Mather’s essay submission ends like this: “We are a species of explorers, and we will meet many setbacks on the way to Mars. However, we can persevere. We — not as a nation but as humans — will not give up. The human race will always persevere into the future.”
Perseverance is an especially apt name for the rover, given that the Mars 2020 team had to deal with a global pandemic in the leadup to launch, NASA officials said.
“Yes, it’s curiosity that pulls us out there, but it’s perseverance that does not let us give up,” Zurbuchen told reporters shortly after the name was announced. “There’s no exploration without perseverance.”
Alabama high schooler Vaneeza Rupani submitted “Ingenuity” for the rover-naming contest. NASA officials liked that moniker so much that they gave it to the mission’s helicopter.
“It took a lot of hard and ingenious work to get the helicopter ready and then placed on the rover, and there’s a lot more going to be required,” Bridenstine said in an April 2020 statement. “I was happy we had another great name from the naming contest finalists from which I was able to select something so representative of this exciting part of our next mission to Mars.”
Additional resources
Explore the Mars 2020 mission in more detail with these resources from NASA and learn more about how the rover was designed. Read about how the Ingenuity helicopter made the first flight on another planet with this informative article by Monica Grady, published on The Conversation.

