It’s a good night for skywatching.
Today (July 28) at 1:55 p.m. EDT (17:55 GMT) the moon officially reached its new moon phase, according to astronomer Chris Vaughan of Astrogeo.ca (opens in new tab), who prepares Space.com’s monthly Night Sky calendar in cooperation with Simulation Curriculum.
The moon will be completely hidden from view anywhere on Earth for about a day, as the new moon is in the same region of sky as the sun and sunlight can only illuminate the far side of the moon, according to Vaughan.
Related: The brightest planets in July’s night sky: How to see them (and when)
After its brief disappearance, “the celestial night-light will return to shine as a crescent in the western evening sky,” writes Vaughan. Until then, skywatchers will enjoy an evening of stargazing completely uninterrupted by moonlight.
The planets Jupiter, Saturn and Mars will all be well-placed for viewing in the early hours of Friday morning (July 29).
Jupiter will be bracketed by reddish Mars off to its left (or celestial northeast) and yellowish Saturn well to its right (or celestial southwest).
(opens in new tab)
Look to the lower eastern sky around midnight to see Jupiter near the border between Pisces and Cetus. The bright gas giant will remain visible throughout the night as it climbs south. Jupiter is an excellent telescope target during July, according to Vaughan. “Its four Galilean moons will dance to the east and west of its banded orb,” Vaughan writes, “which will grow in apparent size from 41 to 45 arc-seconds.”
If you’re looking for a telescope to view the planets our best telescopes for seeing planets guide will help you make an informed decision, while our best telescopes for deep space will help you tour the universe at an even deeper level.
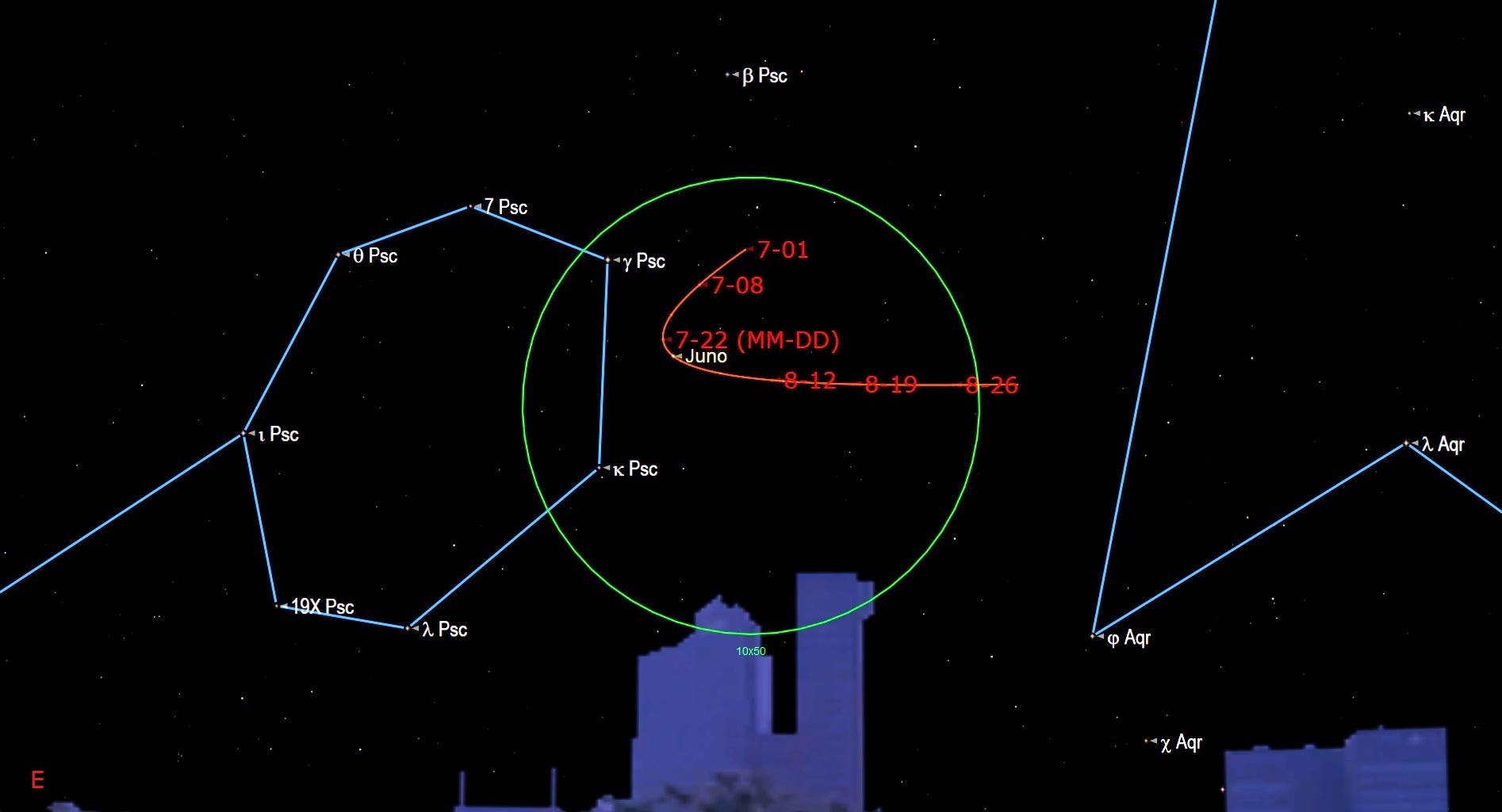
Eagle-eyed skywatchers who fancy a challenge can try and spot the main belt asteroid designated Juno close to the background stars of western Pisces. Juno will appear to slow to a stop then after tonight will commence a westward retrograde loop that will last until late October, according to Vaughan.
(opens in new tab)
Lucky stargazers may also be treated to a meteor show as the Southern Delta Aquariids approach peak activity on Friday (July 29) through dawn on Saturday (July 30). The Delta Aquariids last from July 21 to August 23. Look to the southeastern sky to find the meteor shower‘s radiant — the patch of sky where the meteors will appear to originate from — located in the constellation Aquarius.
Editor’s Note: If you snap a great astrophoto and would like to share it with Space.com’s readers, send your photo(s), comments, and your name and location to [email protected].
Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) and Facebook (opens in new tab).

